OGSM

OGSM makes implementing an ESG strategy more concrete, easier, and more enjoyable!
Introduction
More and more organizations are engaging in sustainability reporting. For some companies, this is driven by the introduction of mandatory sustainability reporting, the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD), while others have already voluntarily started and structured their sustainability reporting based on frameworks such as the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI). Sustainability reporting should ideally be the final step in the cycle of strategy formulation, implementation, internal evaluation, and adjustment. However, in practice, we see that many organizations struggle to establish a clear connection between their ESG strategy, internal management, and external reporting.
Sustainability reporting standards, such as the European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS) and the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI), require organizations to report on how material topics (i.e., impacts, risks, and opportunities) are managed. This includes the policies adopted by the organization, the actions taken and their progress, as well as the objectives and indicators used to determine whether the organization is on the right track. While these standards provide guidelines, they do not prescribe the content of policies and actions, nor do they set specific objectives. However, certain indicators, such as reporting on Scope 1, 2, and 3 emissions, are mandatory. Nevertheless, it remains up to the organization to determine which indicators are relevant for its internal management and external reporting.
In this article, we show how OGSM can help make an organization's ESG strategy concrete and ensure coherence with implementation, internal management, and external reporting.
About OGSM
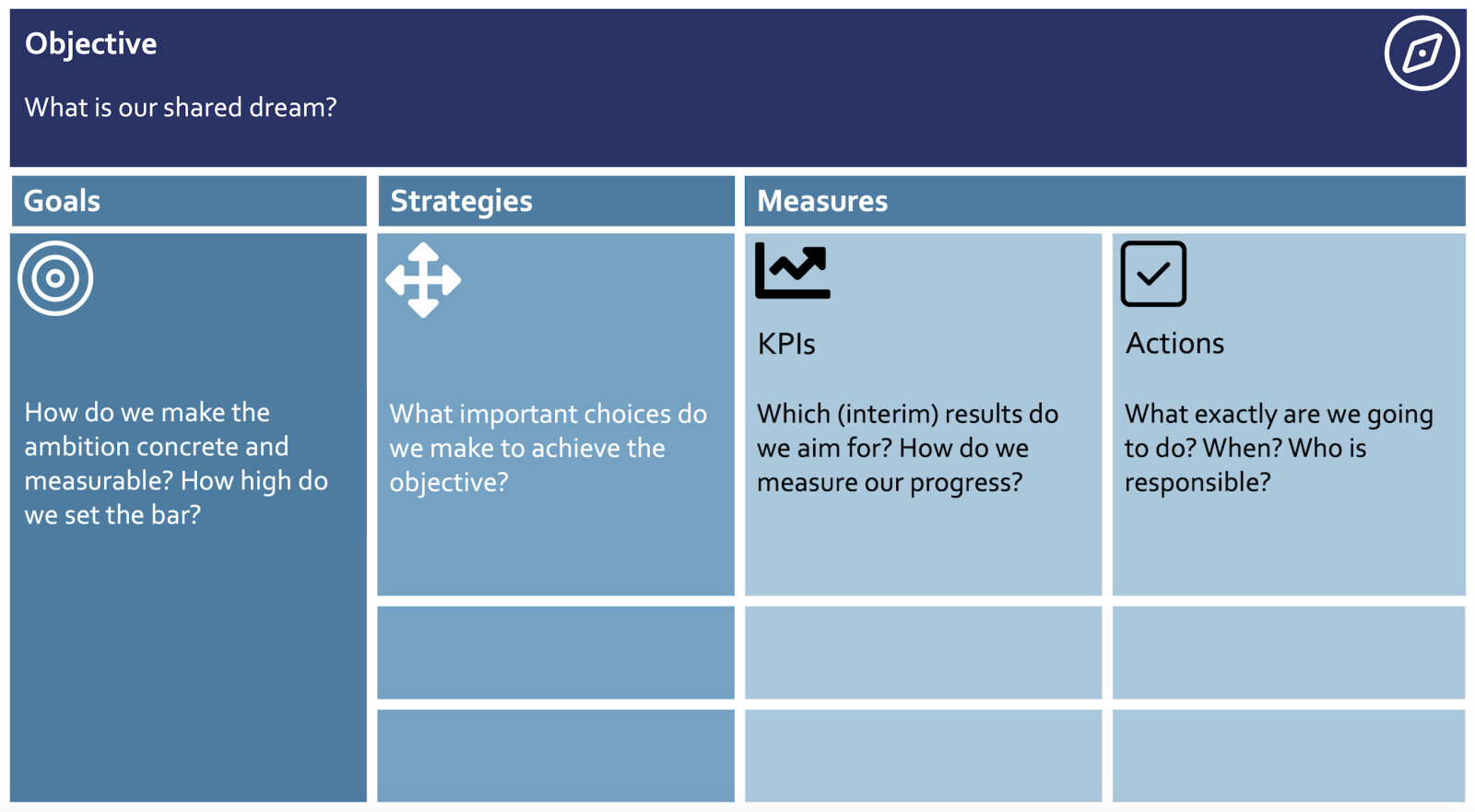
OGSM stands for Objective, Goals, Strategies, and Measures. The core of OGSM is translating long-term ambition into concrete sub-goals and short-term actions within an organization. This ensures that an organization not only knows what it is steering towards but also which daily actions different departments, teams, or programs undertake to realize the objective. The objective (organization’s ambition for the chosen planning period) describes where the organization wants to be in a few years. The goals make this objective measurable and concrete, defining when success is achieved and setting the bar for performance. The strategies form the roadmap to realizing the objective. They determine where the organization invests its people and resources—and where it does not. The measures consist of KPIs and actions. The KPIs monitor the progress of the strategies, while the actions provide quarterly insight into what departments, teams, or programs are concretely doing to make progress on the strategies. OGSM provides organizations with a structured and goal-oriented approach to making their ESG strategy concrete, actionable, and measurable. The OGSM model is shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1: The OGSM Model
The lack of concrete guidance in sustainability reporting requirements
After organizations have conducted a double materiality analysis and identified their material ESG topics, they face the challenge of developing an ESG strategy with concrete actions and monitoring progress using indicators. Reporting standards provide only limited guidelines for this. For example, the CSRD prescribes that organizations must report on gender distribution and age categories of employees under the diversity theme but leaves the choice of indicators for other diversity perspectives or inclusivity up to the organization itself. The same applies to the GRI standards. Organizations must therefore formulate their own policies, actions, goals, and indicators to define their progress on ESG topics and report transparently on them. OGSM offers a structured approach to organizing these elements. It helps organizations make their ESG strategy concrete, bring focus, and create coherence between strategy, policy, goals, indicators, and actions.
The ESG strategy with OGSM in practice
Consider an example of an organization that has the objective (organization’s ambition) to be an industry leader in sustainable and socially responsible business within three years by adopting a circular and inclusive business model with a focus on technological innovation. The goals define how ambitious this objective is. This could include the percentage reduction of Scope 1 and 2 emissions, the share of reused materials in products, the level of inclusivity within business operations, the promotion of employees’ personal development, the number of technological innovations that contribute to reducing the ecological footprint, and the return on ESG investments. The specific goals chosen by the organization depend on the core aspects of its objective, the areas it wants to manage, and the criteria by which its success will be measured.
The strategies indicate the decisions the organization makes to realize its objective. These strategies determine, for example, how CO₂ reduction will be achieved, how circularity and inclusivity within business operations will be increased, how technological innovation will be promoted, how employee personal development will be encouraged, and how transparency and business ethics will be enhanced. The KPIs measure interim progress on these strategies and provide insight into the results the organization aims to achieve. The actions concretely show which steps are being taken to make progress on the strategies. With an OGSM, the ESG strategy becomes concrete, and a clear roadmap is created for achieving the objective. The KPIs and actions clarify which interim results the organization wants to achieve and which specific actions employees are undertaking. This way, the organization establishes a clear link between the ESG strategy, internal management, and external reporting.
Cascading the ESG strategy via OGSM within the organization
Once the OGSM for the ESG strategy has been established, the challenge for organizations lies in its actual implementation. OGSM enables the organization-wide OGSM to be translated into departmental, team, or program-specific OGSMs so that they can concretely contribute to achieving the overarching strategy.
The strategies from the example can be cascaded into underlying OGSMs for departments, teams, or programs. For instance, the strategies for CO₂ reduction can be linked to Finance & Control, technological innovation to R&D, inclusivity to HR, and transparency and business ethics to Compliance. Some strategies, such as circular business operations, may involve multiple departments. In such cases, it may be useful to establish a separate program and link the strategy to it.
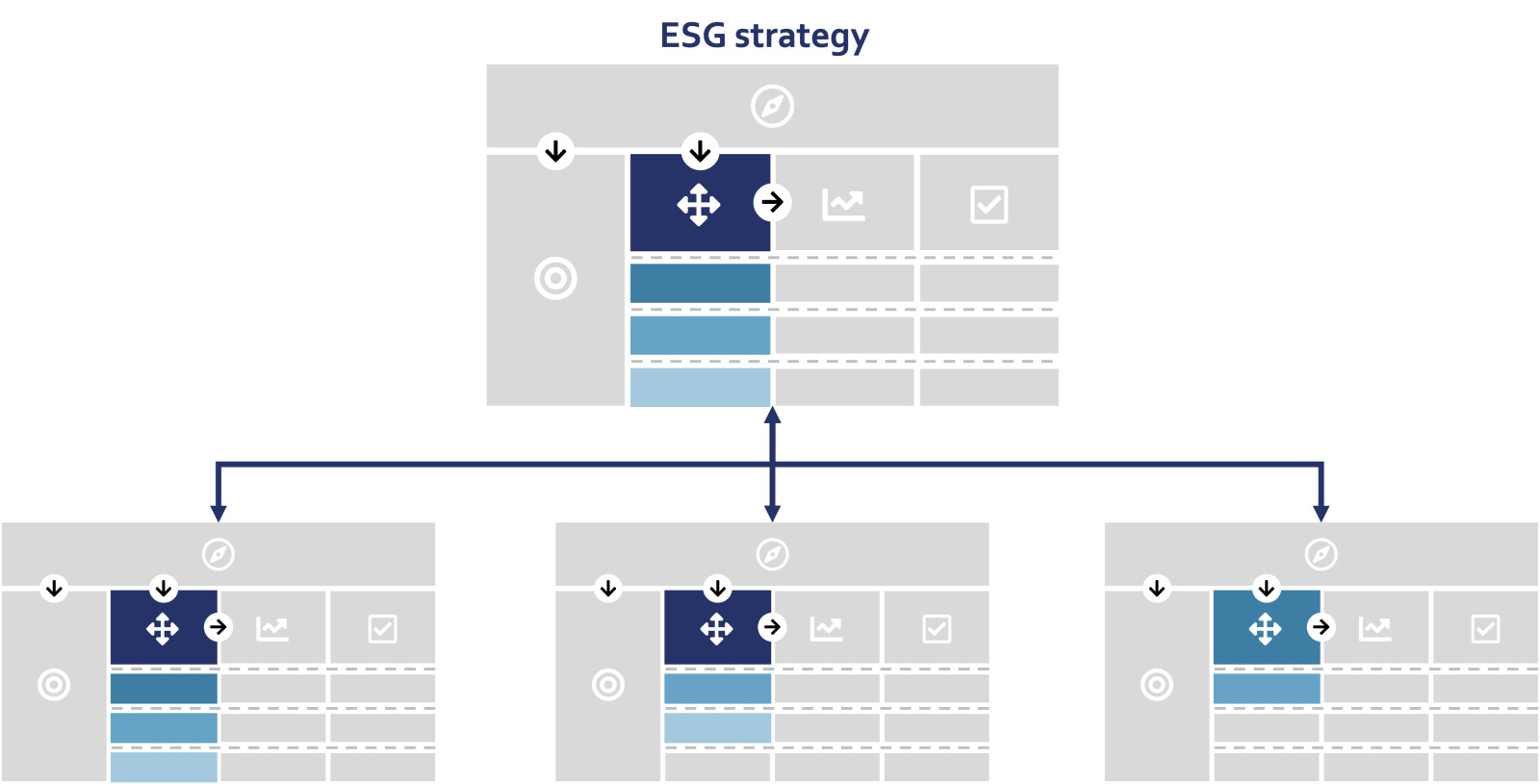
By linking the organization-wide OGSM to underlying OGSMs, the ESG strategy is firmly embedded within the organization, and departments, teams, or programs receive a clear role in realizing the objective. This structured approach ensures that different departments, teams, or programs within the organization contribute to the realization of the ESG strategy in a coordinated manner with concrete actions. At the same time, the organization retains the ability to actively manage implementation and report on progress at the organizational level. Figure 2 illustrates how an ESG strategy can be cascaded within the organization.
Figure 2: Cascading the ESG strategy within the organization
A clear course
In practice, we see that OGSM helps organizations make their ESG strategy concrete. OGSM provides structure and guidance in managing material topics and monitoring progress, making integration into the planning and control cycle easier. By going through the process of developing OGSM(s), employees gain clarity on what they can do daily to contribute to the organization’s sustainability efforts. OGSM clarifies where the organization wants to go, when success is achieved, which roadmap is being followed, and what actions are expected from departments, teams, or programs. This creates a strong connection between the ESG strategy, internal management, and external reporting. It makes the ESG strategy concrete, facilitates decision-making regarding resource allocation, and makes it more engaging for employees to see how their daily actions contribute to the organization’s long-term ESG goals.
Would you like to learn more about OGSM? Read the book ‘OGSM in de Praktijk’ (Dutch).
Get started with your ESG strategy using OGSM
To help companies formulate and implement their ESG strategy, Jester Strategy and 2Impact jointly offer the following:
· April 9 12:00-13:00 hours: Webinar “ESG Strategy with OGSM” – Dutch
· April 16 12:00-13:00 hours: Webinar “ESG Strategy with OGSM” – English
· May: Date TBA – Training “ESG Strategy with OGSM in One Day”
About Jester Strategy
Jester Strategy is the expert on everything strategy. With our insights, innovative methods and tooling we help organisations to be successful in a rapidly changing world. We do not shy away from making distinct and hard choices for the future. For more information: www.jesterstrategy.nl or contact Michiel de Roo!
About 2Impact
2Impact is a boutique consultancy specializing in sustainability strategy, implementation, and reporting. With our diverse team, we bring expertise across all relevant ESG topics. For more information: www.2impact.nl or contact Esther de Graaf!

